What Are You Really Buying When You Invest in AI for Higher Education? A Complete Guide to Making Smart AI Decisions in 2025
by Ardis Kadiu · Oct 08, 2025

In this post, we'll cover:
- What Are the Three Main Types of AI Solutions Available for Higher Education?
- How Do You Evaluate AI Solutions Using the Three Critical Decision Axes?
- What Are the Most Common Mistakes When Buying AI for Higher Education?
What Are the Three Main Types of AI Solutions Available for Higher Education?
Understanding the AI landscape in higher education starts with recognizing that not all AI solutions are created equal. According to Gartner projections, 33% of enterprise applications will include agentic AI by 2028, up from less than 1% in 2024, and higher education institutions need to understand these distinctions now to make strategic investments. Let's break down the three fundamental categories of AI solutions and how they manifest in educational settings.
What Are General AI Assistants and When Should Universities Deploy Them?
General AI assistants are broad chat-based AI tools like ChatGPT, Anthropic Claude, or Google's Gemini that provide wide-ranging support across your institution. These tools live primarily in web browsers, chat applications, or sidebar extensions with minimal integration to your internal systems. They're cloud services accessed through simple interfaces that require little to no setup.
The primary value of general assistants lies in their versatility and immediate availability. They excel at quick ideation, content drafting, question answering, and tutoring across a wide audience. In 2024, 51% of K–12 teachers and 45% of college faculty reported using AI tools, nearly doubling from the previous year, while 86% of students now use AI in their studies. This rapid adoption demonstrates the immediate value these tools provide.
Real-World Implementation Example: Arizona State University's deployment of ChatGPT Edu provides a compelling case study. ASU offers ChatGPT Edu to all students and staff with strict privacy controls, including SSO login, no data retention beyond 180 days, and guarantees that prompts won't be used to train models. This gives broad access to GPT-4 capabilities for writing assistance, tutoring, and research support while maintaining FERPA compliance.
Key Considerations for General Assistants:
- Data Requirements: Minimal to none from internal systems - they come pre-trained on vast datasets
- Integration Complexity: Low - typically plug-and-play with possible SSO integration for enterprise versions
- Governance Watch-outs: Privacy and prompt security are critical, especially regarding FERPA compliance
- Best Use Cases: Campus-wide writing support, general tutoring, brainstorming, research assistance
- ROI Metrics: Measure broad productivity gains, student satisfaction scores, and usage adoption rates
When to Choose General Assistants: Deploy these when you need a broad productivity boost across your institution rather than precise integration with specific workflows. They're ideal as a starting point for AI adoption when you're not ready for deep system integration but want to familiarize your campus with AI capabilities.

In 2024, 51 % of K‑12 teachers and 45 % of college faculty reported using AI tools, while 86 % of students now use AI in their studies.

How Do Co-Pilots and Embedded AI Agents Transform Existing Workflows?
Co-pilots and agents represent context-aware AI helpers embedded directly inside the tools your institution already uses. Unlike general assistants, these AI solutions have local awareness - they can see what users are working on within specific applications and assist accordingly. Think of Microsoft's Copilot in Office 365, Canvas's built-in AI features, or AI assistants integrated into your student information system.
Industry research shows that successful AI deployments often achieve 333% ROI when properly integrated into existing workflows, and co-pilots exemplify this approach by meeting users where they already work.
Where Co-Pilots Live and Operate: Co-pilots exist within the user interface of host applications - email clients, learning management systems, CRM screens, and collaboration platforms. They leverage the data and context of these host applications to provide intelligent assistance. For example, an AI in your email system can read entire conversation threads and draft contextually appropriate replies, while an AI in your CRM knows the student records currently displayed and can suggest next actions.
Microsoft 365 Copilot in Higher Education: When enabled for a university, Microsoft 365 Copilot can automatically draft Outlook emails to students based on their advising history, summarize Teams discussions about curriculum changes, or analyze data in Excel to identify at-risk students. The AI pulls from the actual documents, emails, and data within the Microsoft ecosystem, providing deep contextual understanding.
Canvas LMS AI Integration: Instructure's Canvas now includes AI features that help instructors grade assignments, summarize discussion board posts, and generate quiz questions - all within the familiar Canvas interface. An instructor can click an icon next to a discussion forum, and the AI provides an instant summary of key themes students debated that week, saving hours of reading time.
Critical Value Propositions:
- Reduced context-switching - users never leave their primary workspace
- Higher quality outputs due to contextual data access
- Seamless adoption since the AI appears in familiar interfaces
- Automatic compliance with existing permission models
Implementation Considerations:
- Data Needs: Strong, context-specific access to application data
- Integration Complexity: Medium - often requires configuration and testing
- Governance Requirements: Must respect role-based access controls and verify AI accuracy within trusted interfaces
- Key Risk: Hallucinations presented as facts within official systems
When to Deploy Co-Pilots: Research indicates that 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, with IT and marketing/sales being the most common starting points. Choose co-pilots when most work happens in a few major software environments and you want to augment those existing workflows rather than create new ones.

Industry research shows that successful AI deployments often achieve a 333 % ROI when AI is embedded in existing workflows.

What Are Workflow AI Agents and How Do They Transform End-to-End Processes?
Workflow AI represents the most sophisticated category - AI that orchestrates and automates multi-step processes across multiple systems, functioning as autonomous or semi-autonomous agents. These solutions go beyond suggesting or drafting; they take actions, update records across systems, trigger processes, and loop in humans only when necessary.
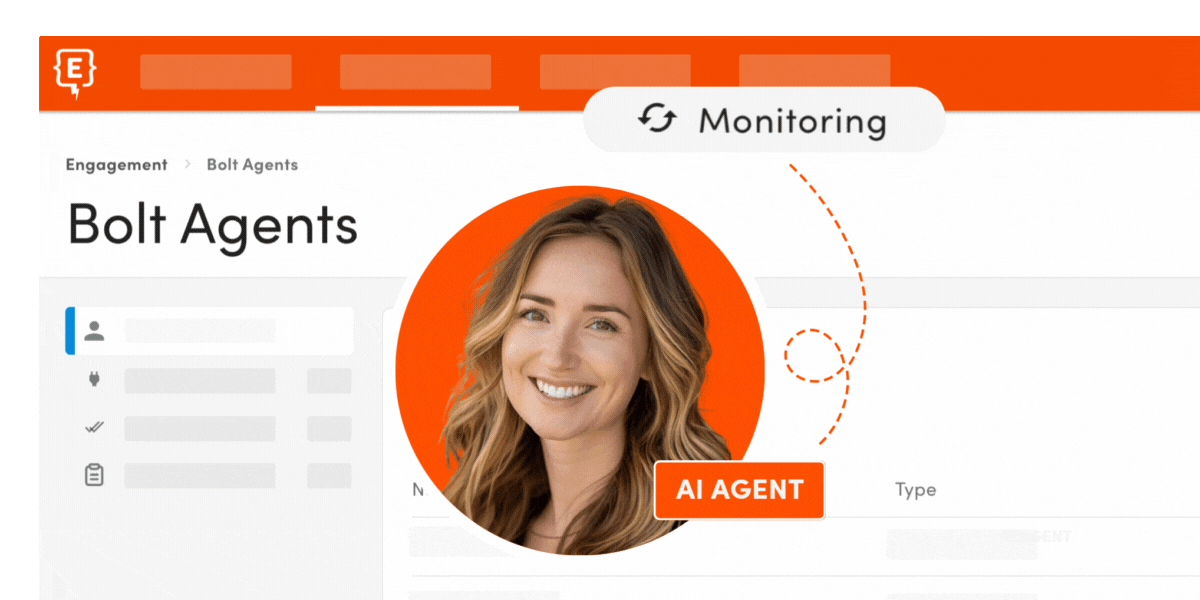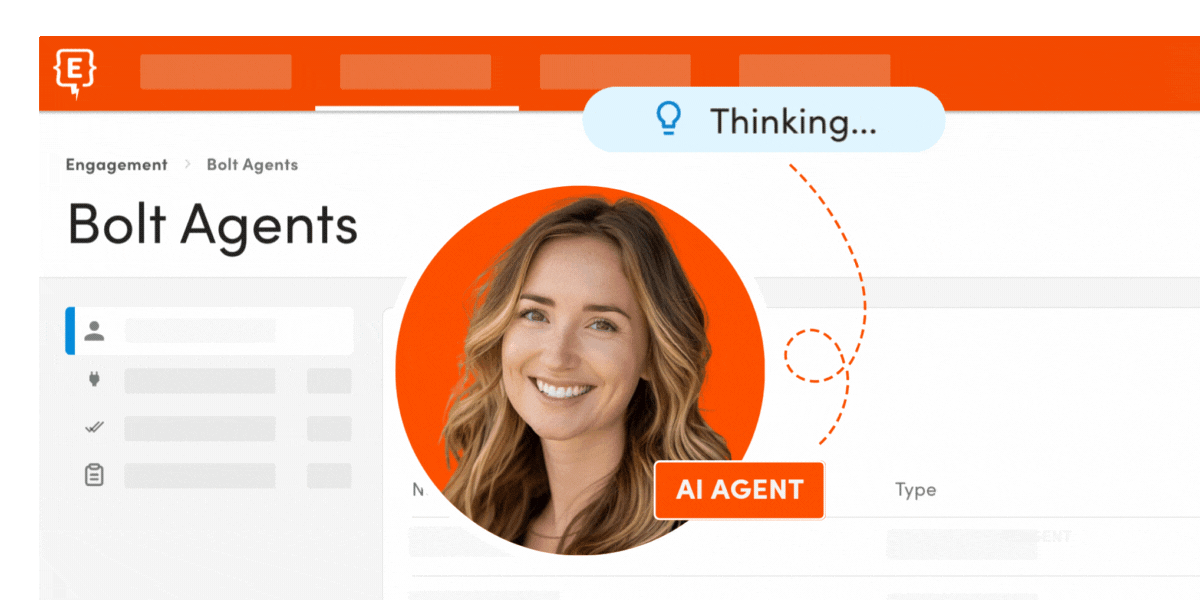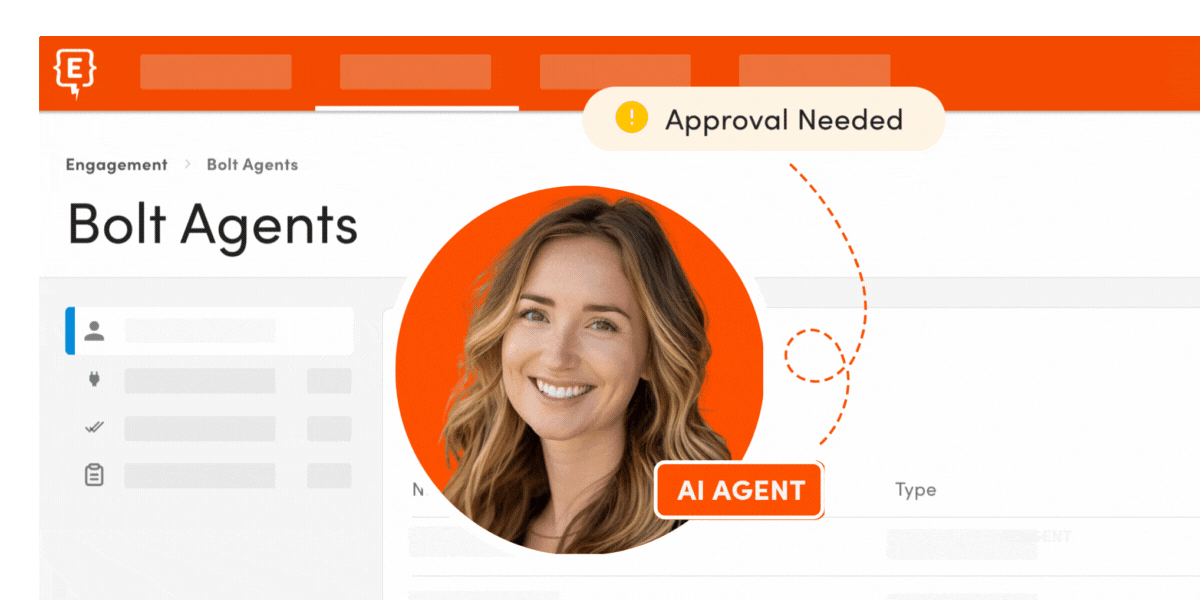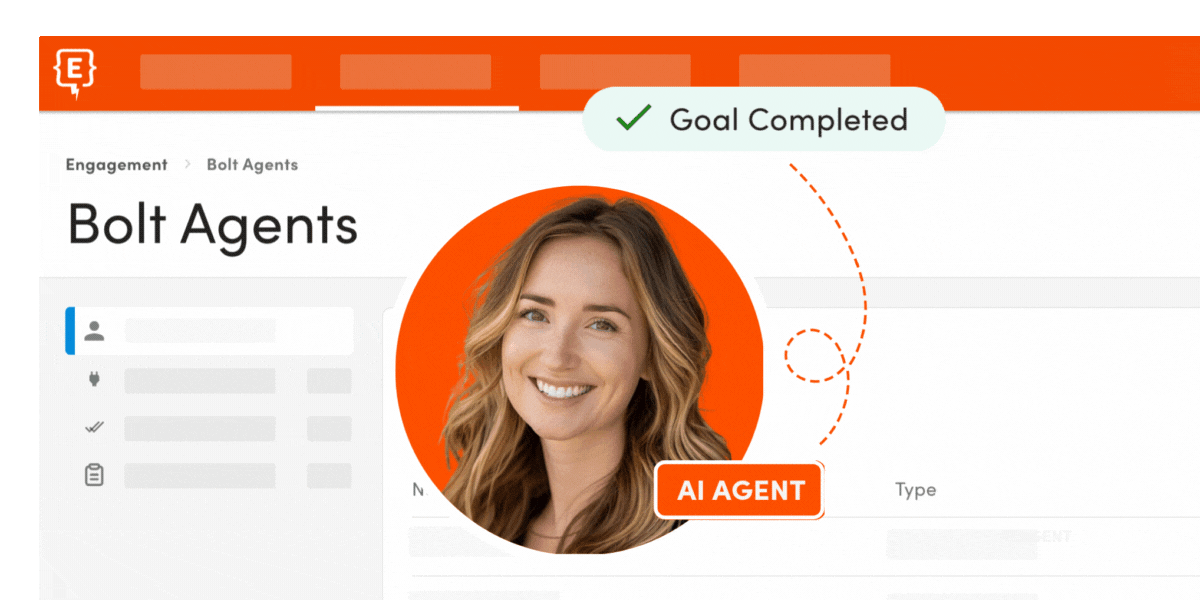
Element451's Bolt Agents exemplify this category, serving as "digital teammates that read applications, answer every question, and drive student success with proactive nudges—working with your CRM today". These agents don't just assist; they complete entire workflows autonomously.
Where Workflow AI Lives: These agents operate deep in your operational stack, often as integrations via APIs, automation platforms, or agent frameworks. They might run on servers, listening for events (like "new application submitted") and then executing chains of actions. While they may include user-facing chat components, their primary value comes from backend process automation across your CRM, SIS, LMS, and other core systems.
Element451 Bolt Agents in Action: Element451's Bolt Agents are "proactive, goal-oriented teammates designed to support overextended staff—not replace them". Here are specific examples of how they transform workflows:
- Admissions Processing Agent: Element451's admissions agents perform rubric-based first reads with human-readable rationales, achieving 94% model-to-human agreement and flagging 186 fraudulent applications in one week at Kellogg Community College. The agent reads applications, verifies documents, scores based on institutional rubrics, and routes files for human review - completing in minutes what traditionally takes hours.
- Enrollment Management Agent: Imagine assigning an AI agent the goal of getting 500 newly admitted Health Sciences students registered for fall. The agent works autonomously to identify unregistered students, send personalized outreach, answer questions, help with course selection, and track progress - reporting back that 537 students enrolled without human intervention.
- Student Success Agent: The Academic Advisor Agent monitors student progress, identifies at-risk indicators, and sends personalized nudges to keep students on track. It might notice a student hasn't registered for next term, reach out with customized messaging, help resolve holds or issues, and ensure registration completion - all while keeping advisors informed.
Real-World Results:
- One institution reported a 24% decrease in call volume and 10% increase in enrollment after deploying Element451's BlazeBot AI assistant
- Another saved approximately 160,000 minutes of staff time through intelligent admissions automation
- CollegeVine's AI Recruiter helped colleges achieve a 32% increase in admission rates by autonomously engaging prospects and guiding them through application steps
- Berry College and Knox College use AI recruiters to identify students who haven't submitted financial aid forms, reach out individually, help complete FAFSA, and report back
Unity University partnered with Salesforce's Agentforce to deploy "Una," a chatbot that guides prospective students and will automatically fill out college applications based on chat interactions
Critical Implementation Factors:
- Data Requirements: High - requires bi-directional sync across multiple systems
- Integration Complexity: High - demands IT resources and multi-vendor coordination
- Governance Needs: Comprehensive audit trails, exception handling, security controls
- Change Management: Significant - may alter job roles and departmental processes
When to Invest in Workflow AI: With 62% of organizations expecting over 100% ROI from agentic AI deployment and U.S. companies projecting 192% returns, workflow AI makes sense when you can clearly articulate specific processes with measurable KPIs that span multiple systems. Green-light these investments when you have a process owner, clear metrics, and organizational readiness for transformation.

Element451’s admissions agents perform first‑read reviews with 94 % model‑to‑human agreement and flagged 186 fraudulent applications in one week at Kellogg Community College.

How Do You Evaluate AI Solutions Using the Three Critical Decision Axes?
When evaluating AI solutions for your institution, you need a framework that cuts through vendor hype and focuses on what actually matters. Three fundamental axes help you plot where any AI solution sits in your landscape and whether it's the right fit for your needs. Let's explore each axis with detailed examples and evaluation criteria.
Axis 1: What Is Data Gravity and Why Does it Determine AI Success?
The Core Question: "Where does the source-of-truth data reside that this AI needs to read or write?"
Data gravity refers to the tendency of applications and services to be attracted to data, much like objects are attracted by gravity. In the context of AI for higher education, this means AI performs best when operating as close as possible to your cleanest, most governed data sources.
Understanding Your Data Landscape: Every institution has systems of record - your CRM holds prospective student data, your SIS contains enrollment and academic records, your LMS houses course content and gradebooks. The closer an AI solution operates to these primary data sources, the more value it can deliver.
Element451's Approach to Data Gravity: Element451's Bolt Agents are "fully integrated into the Element451 CRM" and "use the data, goals, and context already in Element451" with "no third-party software to stitch together or babysit". This tight integration means agents have immediate access to all student interactions, campaign history, and engagement metrics without complex data pipelines or synchronization delays.
Red Flags - The "Smart Wrapper" Trap: Beware of solutions that appear intelligent but lack true integration. Signs of a wrapper include:
- AI that can only access data through screen scraping or periodic CSV exports
- Systems that require manual data uploads to function
- Tools that can read but not write back to your systems of record
- Solutions dependent on copying data to external clouds for processing
Research shows that companies struggle when AI isn't properly integrated, with only 31% of leaders able to evaluate ROI within six months. Much of this challenge stems from weak data integration.
Evaluation Framework for Data Gravity:
- Direct Integration Test: Can the AI read and write directly to your core systems via APIs?
- Data Freshness Check: Is the AI working with real-time data or periodic snapshots?
- Completeness Assessment: Does the AI have access to all relevant data fields, or just a subset?
- Governance Alignment: Does the AI respect your existing data governance and permission models?
Practical Example: Consider two AI advising solutions. Solution A is embedded in your CRM and can instantly access a student's complete interaction history, academic progress, and engagement metrics. Solution B is a standalone chatbot that requires daily data exports from your SIS and can't update records directly. Solution A's proximity to data gravity means it can provide more accurate, timely, and actionable guidance while automatically maintaining data consistency.
Axis 2: Where Does the AI Take Action in Your Processes?
The Core Question: "What is the last mile of this AI's output - is it advising, drafting, or actually executing tasks?"
The action surface determines how close to actual decisions and outcomes the AI operates. This axis ranges from passive suggestions to autonomous execution, with profound implications for both value creation and risk management.
Three Levels of Action Surface:
Level 1 - Advice in Chat (Lowest Action Surface): The AI provides suggestions or answers in a conversational interface, but humans must translate these into actions. Think of an AI that says, "This student appears at risk of dropping out based on engagement metrics," but requires staff to decide what to do with that information.
Level 2 - Drafting Within Applications: The AI creates concrete deliverables within your workflow but requires human approval. Examples include:
- Drafting emails in your communication platform that staff review and send
- Pre-filling application evaluation forms for counselors to verify
- Generating draft course content that instructors refine
Element451's agents can work at this level, where "staff can review, edit, and approve the agent's work—just like they would with a junior colleague".
Level 3 - Autonomous Execution (Highest Action Surface): The AI completes entire processes independently, potentially across multiple systems. Element451's Bolt Agents exemplify this level: "Built to crush the admissions grind, Bolt Agents handle file completion, fraud checks, app scoring, and decisioning—so your staff can focus on high-touch yield, not paperwork".
ROI Correlation with Action Surface: Organizations achieving optimal ROI from AI report that success comes from moving beyond advice to actual automation, with labor cost reductions and operational efficiency gains as key value drivers. The closer AI gets to actual execution, the higher the potential ROI - but also the greater need for governance.
Risk-Value Assessment Framework:
- Low Risk/Low Value: AI chatbot that answers FAQs
- Medium Risk/Medium Value: AI that drafts personalized communications for approval
- High Risk/High Value: AI that autonomously processes applications and makes initial admit decisions
When to Choose Each Level:
- Start with Level 1 when exploring new use cases or when stakeholder trust is low
- Move to Level 2 when you have validated AI accuracy and want efficiency gains
- Advance to Level 3 only after establishing robust governance and achieving consistent success at Level 2
Axis 3: How Autonomous Should Your AI Agents Be?
The Core Question: "Should the AI suggest, assist with oversight, or act independently?"
Autonomy differs from action surface by focusing on the AI's independence rather than where it operates. We can define a clear spectrum:
The Autonomy Spectrum:
- S0: No Autonomy - Traditional software requiring explicit human commands
- S1: Suggest - AI provides recommendations but takes no action
- S2: Assist with Oversight - AI acts but requires human approval
- S3: Act Autonomously - AI executes independently within defined parameters
The Golden Rule: Never jump directly from S0 to S3. Research emphasizes that successful AI deployment requires gradual autonomy increases with proper checkpoints, as organizations must build trust through incremental success.
Element451's Graduated Approach: Element451 demonstrates this principle in practice. Their Bolt Agents can operate at different autonomy levels based on institutional comfort:
- S1 Mode: Agents analyze data and suggest which students need outreach
- S2 Mode: Agents draft communications and present them for staff approval
- S3 Mode: Agents autonomously engage prospects, answer questions, and guide them through processes
The Trust Ladder Framework:
- Month 1-2: Run AI in suggestion mode (S1) to validate accuracy
- Month 3-4: Enable assisted mode (S2) with required approvals
- Month 5-6: Allow autonomous action (S3) for low-risk, high-frequency tasks
- Month 6+: Expand autonomous scope based on demonstrated success
Critical Checkpoint Questions: Before increasing autonomy, answer these questions:
- Has the AI maintained 95%+ accuracy at the current level for at least 30 days?
- Do we have clear rollback procedures if something goes wrong?
- Have we defined explicit boundaries for AI decision-making?
- Is there an audit trail for every AI action?
- Do stakeholders understand and accept the AI's role?
Case Study in Autonomy Management: When Element451 partner institutions deploy enrollment agents, they often start by having agents identify unregistered students (S1), then progress to drafting outreach messages for review (S2), and finally allow autonomous communication within defined parameters (S3). This graduated approach builds institutional confidence while delivering incremental value.
What Are the Most Common Mistakes When Buying AI for Higher Education?
Even with a clear understanding of AI categories and evaluation frameworks, institutions frequently fall into predictable traps when selecting AI solutions. Let's examine the three most costly mistakes and how to avoid them, using real-world examples and prevention strategies.
Mistake #1: The Wrapper Trap - When Is AI Integration Real Versus Cosmetic?
What It Looks Like: The wrapper trap occurs when vendors offer a ChatGPT-like overlay that supposedly "knows your organization" but lacks genuine integration. In demos, these solutions appear magical - answering questions about your data in plain English. But the magic is often an illusion.
How to Spot a Wrapper: Watch for these warning signs during vendor demonstrations:
- The AI can read some data but can't write anything back to your systems
- Data access relies on periodic exports, web scraping, or manual uploads
- The vendor can't clearly explain their data pipeline architecture
- There's a separate interface rather than integration with existing tools
- Response accuracy degrades significantly with edge cases or complex queries
Real-World Consequences: Research shows that 85% of leaders cite data quality as a primary concern with AI implementations, often because solutions aren't properly integrated with source systems. Institutions that buy wrappers typically experience:
- Low adoption rates after initial novelty wears off
- Frequent inaccuracies due to stale or incomplete data
- Staff frustration from having to correct AI mistakes
- Hidden costs from maintaining data pipelines and exports
- Security vulnerabilities from data duplication
The Element451 Counter-Example: Element451's approach demonstrates true integration: their Bolt Agents are "fully integrated into the Element451 CRM" with the data and context "already in Element451". This means agents can instantly access complete student histories, update records in real-time, and maintain data consistency without external synchronization.
Prevention Strategy - The Integration Test: Before committing to any AI solution, demand clear answers to these questions:
- Data Flow Diagram: Can the vendor draw exactly how data moves between your systems and their AI?
- API Documentation: What specific APIs or integration methods does the solution use?
- Write-Back Capability: Can the AI update your source systems, not just read from them?
- Latency Check: How long between a change in your system and AI awareness of that change?
- Permission Model: How does the AI inherit and respect your existing security model?
Red Flag Response Examples:
- "Our AI learns from your website and documentation" (Translation: No real integration)
- "We'll need periodic data exports in CSV format" (Translation: Batch processing, not real-time)
- "The AI has its own knowledge base we maintain" (Translation: Duplicate data and synchronization issues)
Green Flag Response Examples:
- "We integrate via authenticated APIs with real-time data access"
- "The AI operates within your existing permission structure through SSO"
- "All AI actions are logged in your system of record with full audit trails"

62 % of organizations expect over 100 % ROI from agentic AI deployments, and U.S. companies project 192 % returns; yet 88 % of AI pilots never reach production.

Mistake #2: The Pilot Purgatory - Why Do 88% of AI Pilots Never Reach Production?
The Sobering Reality: Studies show that while 62% of organizations expect 100%+ ROI from AI deployments, actual success rates remain low, with over 88% of AI pilots never making it to production. Higher education faces particular challenges with extended pilot phases that consume resources without delivering value.
Common Pilot Failure Patterns:
The Eternal Science Experiment: Your institution runs an "innovative" pilot with a promising AI tool for student sentiment analysis. Six months later, you're still "evaluating" with no clear path to implementation. The pilot becomes a permanent sandbox that never influences real operations.
The Compelling Demo Syndrome: A vendor demonstrates their AI identifying at-risk students with impressive accuracy. You sign up for a pilot, but discover:
- The demo used cleaned, historical data rather than messy, real-time information
- Integration with your actual systems is far more complex than shown
- The AI requires extensive configuration for your specific context
- Compliance and security reviews reveal unexpected obstacles
The Resource Black Hole: What starts as a "simple pilot" evolves into a major project requiring:
- Dedicated IT resources for integration and maintenance
- Staff training that pulls people from regular duties
- Ongoing vendor management and troubleshooting
- Regular reports to justify continued investment
Why Element451's Approach Works: Element451's Bolt Agents are "available now and already in use by Element451 partner institutions", moving beyond perpetual pilots to actual deployment. Their approach includes:
- Pre-built agents for common use cases (admissions, advising, engagement)
- Proven integration patterns with existing higher ed systems
- Clear success metrics tied to institutional KPIs
- Rapid deployment timelines measured in days, not months
The Pilot-to-Production Framework:
Before Starting Any Pilot:
- Define specific success criteria with quantifiable metrics
- Set a firm end date (typically 60-90 days maximum)
- Identify the production deployment path and requirements
- Allocate resources for full implementation, not just testing
- Establish go/no-go decision criteria and timeline
During the Pilot:
- Track metrics weekly, not monthly
- Document integration requirements and pain points
- Gather user feedback through structured surveys
- Calculate actual ROI based on time and resources invested
- Identify scaling requirements and costs
The 30-60-90 Day Framework:
- Days 1-30: Technical integration and initial configuration
- Days 31-60: Active testing with real users and use cases
- Days 61-90: Performance evaluation and go/no-go decision
Critical Decision Point: At 90 days, you must either commit to production deployment with allocated budget and resources, or end the pilot completely. No extensions without exceptional justification.
Success Story Framework: Kellogg Community College's pilot with Element451 achieved clear results: 94% model-to-human agreement on application reviews and 186 fraud cases identified in one week. This wasn't an endless experiment but a focused validation with measurable outcomes leading to production deployment.

62 % of organizations expect over 100 % ROI from agentic AI deployments, and U.S. companies project 192 % returns; yet 88 % of AI pilots never reach production.

Mistake #3: The Lone Wolf Tool - How Do Siloed AI Solutions Fragment Your Ecosystem?
The Proliferation Problem: As different departments discover AI solutions for their specific needs, institutions accumulate disconnected tools:
- Admissions buys an AI application reviewer
- Student Success implements an AI early alert system
- The Registrar adopts an AI transcript processor
- Financial Aid deploys an AI verification tool
- Marketing uses an AI content generator
Suddenly, you have five different AI systems with separate logins, data silos, and no coordination.
The Hidden Costs of Fragmentation:
Data Inconsistency: Each AI tool maintains its own version of "truth" about students. The admissions AI thinks a student is enrolled, while the advising AI shows them as prospective. Staff spend hours reconciling differences instead of serving students.
User Fatigue: Research shows adoption rates drop significantly when users must navigate multiple AI interfaces, with larger organizations particularly struggling with tool proliferation. Staff resist learning yet another system, especially when benefits are marginal.
Integration Nightmares: Every lone wolf tool requires its own:
- Data pipeline and synchronization process
- Security review and compliance documentation
- Vendor management and support relationship
- Training program and documentation
- Budget line item and renewal cycle
Missed Optimization Opportunities: Siloed AIs can't share insights or coordinate actions. The admissions AI doesn't know what the advising AI discovered about student preferences. The financial aid AI can't inform the retention AI about risk factors.
The Platform Advantage - Element451's Unified Approach: Element451 addresses fragmentation through a platform strategy where multiple Bolt Agents work together: "From prospect to post-graduation, Element451 helps schools connect with students in smarter, faster, and more personal ways".
Their integrated agent ecosystem includes:
- Admissions Agents: Application processing, fraud detection, scoring
- Engagement Agents: Personalized outreach, campaign management
- Student Success Agents: Retention monitoring, proactive intervention
- Service Agents: 24/7 question answering across all channels
All agents share the same data model, permission structure, and user interface, eliminating fragmentation while providing specialized functionality.
Fragmentation Prevention Checklist:
Before adding any new AI tool, evaluate:
- Overlap Assessment: Does this functionality exist in current systems?
- Integration Capability: Can this tool share data with existing platforms?
- Platform Potential: Could this need be met by extending current AI investments?
- Total Cost of Ownership: What are the full costs including integration and maintenance?
- User Impact: How many additional systems will users need to learn?
The Consolidation Strategy: Rather than accumulating point solutions, consider:
- Choosing a primary AI platform that can expand to meet multiple needs
- Requiring all AI tools to integrate with your core systems of record
- Establishing an AI governance committee to evaluate all new tools
- Creating a roadmap for consolidating existing tools into fewer platforms
Success Metric: Organizations achieving the highest AI ROI focus on platform approaches rather than point solutions, with 49% of technology leaders reporting AI is "fully integrated" into their core business strategy. Aim for comprehensive platform coverage rather than best-of-breed point solutions.
Join the AI Transformation Movement
The window for competitive advantage through AI in higher education is narrowing. With the AI education market projected to grow from $7.57 billion in 2025 to $112.30 billion by 2034, institutions that act now will shape the future of education, while those that wait risk being left behind.
As Element451's Engage Summit demonstrates, this is "where transformation happens. Where bold ideas meet real solutions. Where AI stops being hype and starts driving results". The question isn't whether to adopt AI, but how quickly and effectively you can harness its power to serve your students and transform your institution.
Enrollify's research shows that "AI is not just a trend—it's a fundamental shift in how higher education institutions operate". From automating student lifecycle management to revolutionizing enrollment marketing and engagement strategies, AI is shaping the future of higher ed.
Stay tuned for our next installment where we'll take you step-by-step through the 90-day pilot playbook, complete with templates, checklists, and real-world case studies of pilots that successfully scaled to transform entire institutions.
Remember: You're not just buying AI – you're buying transformation. Make sure you know exactly what you're getting, where it will have impact, and how you'll measure success. The institutions that get this right will thrive in the AI-powered future of higher education.

94 % of organizations say that orchestrating processes is essential for AI success, and 49 % of technology leaders report AI is now fully integrated into their core business strategy.

Ready to explore how AI agents can transform your institution? Learn more about Element451's Bolt Agents and discover how institutions are already achieving measurable results with their AI workforce.
For hands-on training with AI implementation in higher education, consider attending the AI Engage Summit or exploring Enrollify's comprehensive resources on AI in higher education.
Join the conversation about AI transformation in higher education by subscribing to Enrollify's Higher Ed Pulse podcast and staying updated on the latest AI trends and research.

About Element451
Boost enrollment, improve engagement, and support students with an AI-driven CRM and agent platform built for higher ed. Element451 makes personalization scalable and success repeatable.
Categories
New Blog Posts
The Definitive Guide
AI in Higher Education
Bridge the gap between the latest tech advancements and your institution's success.
Useful Links
Related Articles

Talk With Us
Element451 is an AI-driven CRM and AI agent platform for higher education. Our friendly experts are here to help you explore how Element451 can improve outcomes for your school and students.
Get a Demo